Focus
Prevention
Overview
We place a strong emphasis on proactive health management, aiming to support optimal wellness before issues arise. Our key focus areas in precautionary care include:
General Health Maintenance Comprehensive care designed to preserve and enhance your overall well-being through early detection, lifestyle guidance, and personalized health strategies.
Stress Diagnostics & Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Analysis Advanced tools and methods to evaluate how stress is affecting your body, including HRV measurements that offer insight into nervous system resilience, recovery capacity, and autonomic balance.
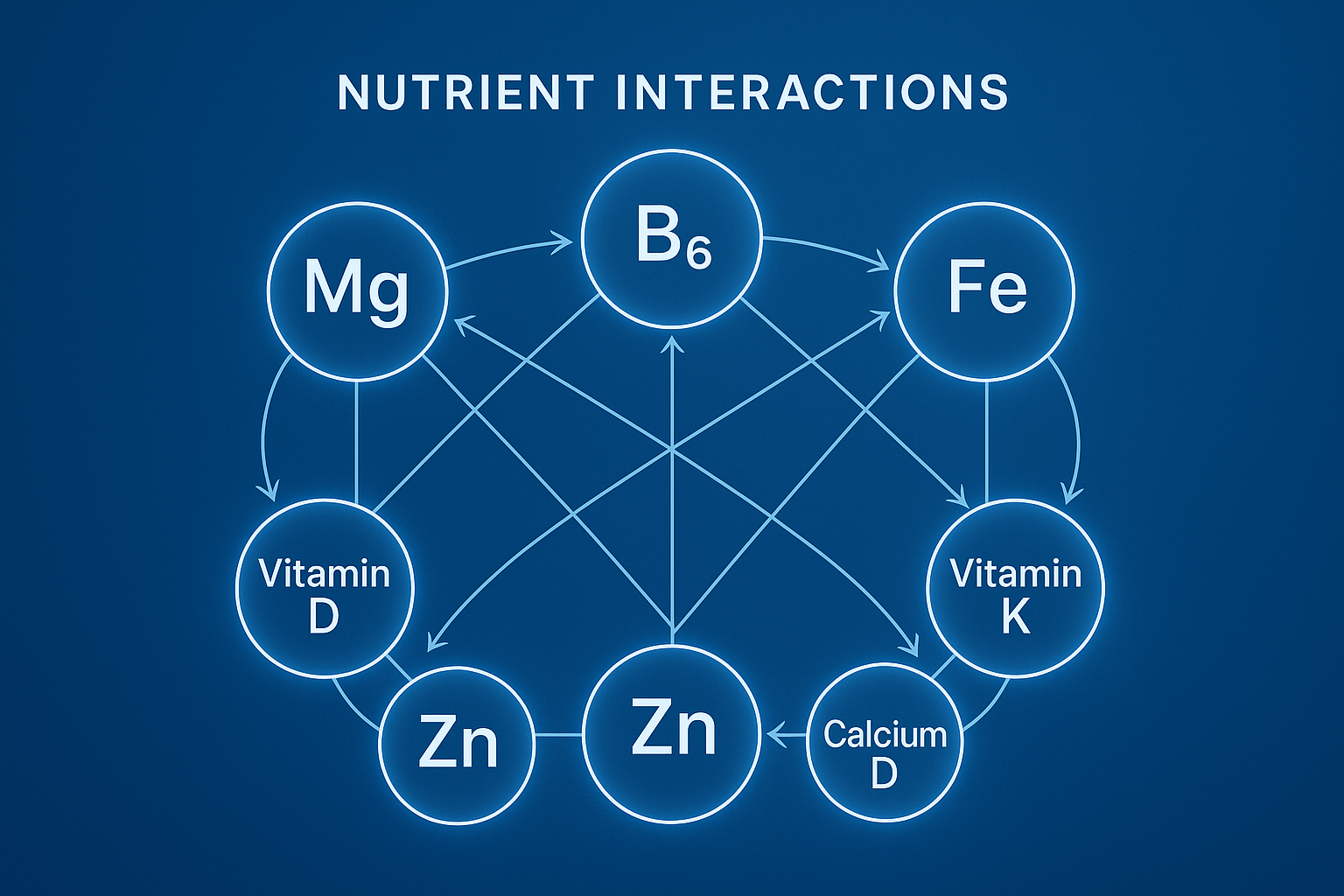
Macro and Micronutrient Profiling Targeted diagnostics to assess nutritional imbalances or deficiencies—ensuring your body has the essential building blocks for sustained energy, immunity, and cellular function.
Our Preventive & Longevity-Informed Approach
At our integrative medicine practice, prevention is the foundation of our work. We combine insights from modern longevity research, systems biology, and holistic health sciences to help individuals design lifestyles that support long-term resilience, adaptability, and wellbeing.
Contemporary findings in aging science suggest that the way we live—how we eat, move, sleep, manage stress, and interact with our environment—can influence key biological processes associated with cellular function, repair, and long-term vitality. These include pathways related to mitochondrial efficiency, circadian rhythm regulation, cellular maintenance cycles, and metabolic flexibility.
Naturheilkunde Integrated With Modern Longevity Science
Drawing from German Naturheilkunde, we integrate structured, nature-informed principles such as regulated daily rhythms, functional movement, nutrient-focused dietary patterns, evidence-aligned restorative practices, and environmentally oriented stress-modulation strategies. Together, these elements provide a systematic framework for informed lifestyle design and proactive self-regulation.
These principles complement modern longevity insights showing that environmental signals—light exposure, temperature variation, nutrition timing, and movement patterns—can influence cellular processes such as repair cycles, circadian gene expression, and metabolic adaptation.

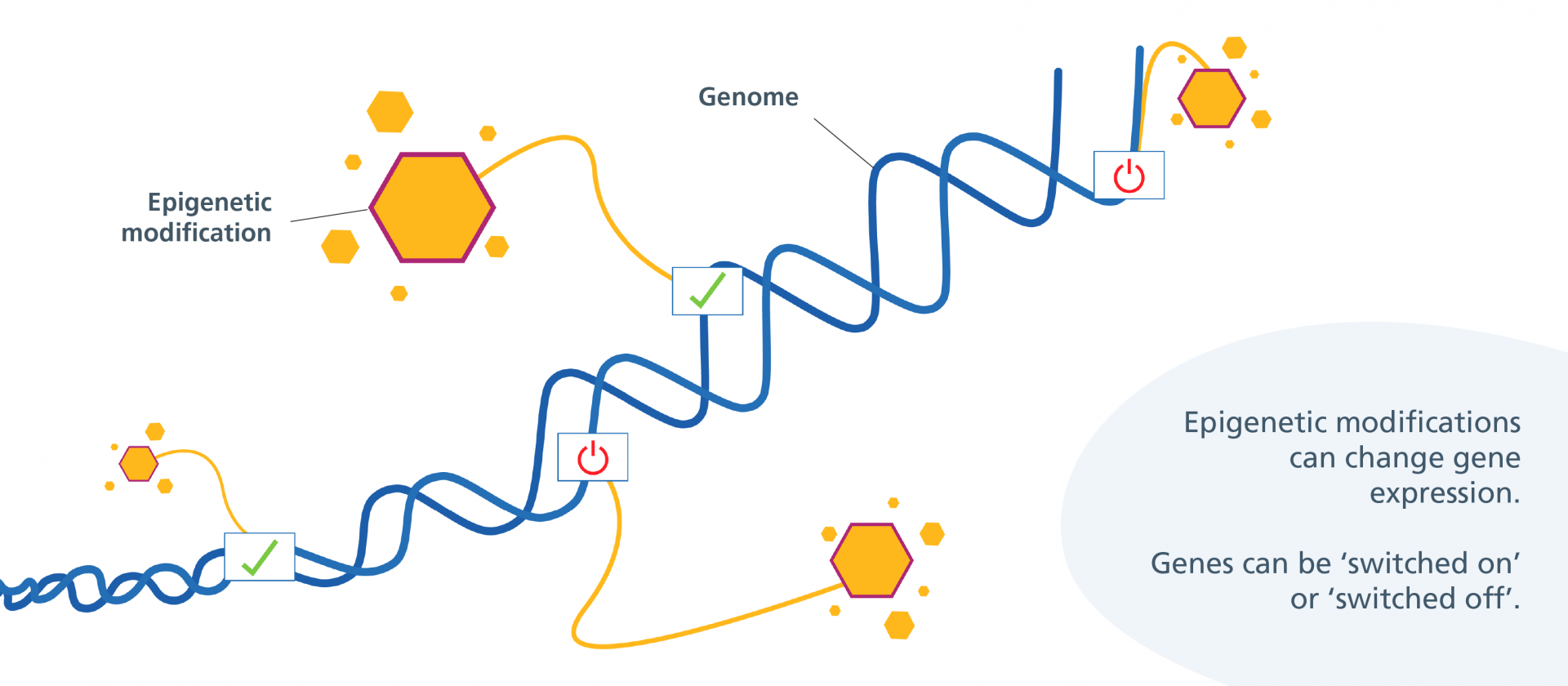
Epigenetics: How Lifestyle Interacts With Biology
Epigenetic research demonstrates that environmental and behavioral inputs can influence gene activity over time. Factors such as nourishment, stress exposure, sleep quality, and physical activity shape how cells respond, maintain, and adapt across the lifespan. This underscores the importance of intentional, biologically aligned routines.
Neuroscience: The Brain as a Regulator of Long-Term Wellbeing
Neuroscience shows that the brain continuously adapts through neuroplasticity. Stress response patterns, motivation, focus, and habit formation all evolve with repeated behaviors. Aligning lifestyle practices with how the nervous system learns and adapts enables individuals to cultivate stable routines that support emotional regulation, cognitive function, and long-term behavioral consistency.

Inflammaging: A Key Concept in Modern Aging Science
A central idea in longevity research is inflammaging, a term describing the gradual increase in low-grade, systemic inflammatory activity observed with advancing age. Originally introduced by immunologist Claudio Franceschi, the concept highlights how immune system shifts, cellular senescence, metabolic stress, and environmental exposures can contribute to a persistent inflammatory background over time.
While inflammaging is a natural feature of biological aging, research indicates it is shaped by long-term patterns—sleep, stress, nutrition, movement, environmental inputs, and circadian alignment. This makes prevention particularly relevant: consistent, supportive daily habits may help reduce unnecessary biological stressors and contribute to a more balanced internal environment over the lifespan.

Cellular Renewal & Apoptosis (Educational Context)
Longevity science also explores how cells maintain equilibrium through processes such as autophagy (cellular recycling) and apoptosis (programmed turnover). These mechanisms are influenced by signals like circadian timing, nutrient cycles, movement, and stress modulation. Our approach supports individuals in creating lifestyle environments that align with these insights, helping regulate and harmonize natural maintenance and renewal rhythms.
The Role of Thoughtful Supplementation
Supplementation can be a supportive tool within a longevity-informed lifestyle. Evidence-aligned micronutrients and bioactive compounds may help refine nutritional intake, especially when environmental conditions, stressors, or increased demands influence nutrient availability. Our guidance emphasizes individualized, science- and research-based use so supplementation integrates responsibly within broader preventive strategies.
Why a Longevity-Focused Preventive Approach Matters
- Aging follows biological patterns influenced by daily behaviors. Research across epigenetics, immunology, and cellular biology shows that consistent lifestyle inputs shape long-term trajectories.
- Processes like inflammaging develop over decades. Early, supportive routines may help reduce cumulative stressors that contribute to age-related biological shifts.
- Biological systems rely on rhythmic signals. Circadian science highlights the importance of predictable timing cues for energy regulation, cognitive performance, and cellular maintenance.
- Neural and metabolic pathways evolve with repetition. Consistent habits, rather than occasional interventions, influence long-term adaptability and resilience.
- Longevity research emphasizes proactive design over reactive responses. Constructing environments and routines aligned with biological needs offers a practical foundation for sustained long-term wellbeing.

